
In many cases, a person does not need to do anything to treat a blood blister.

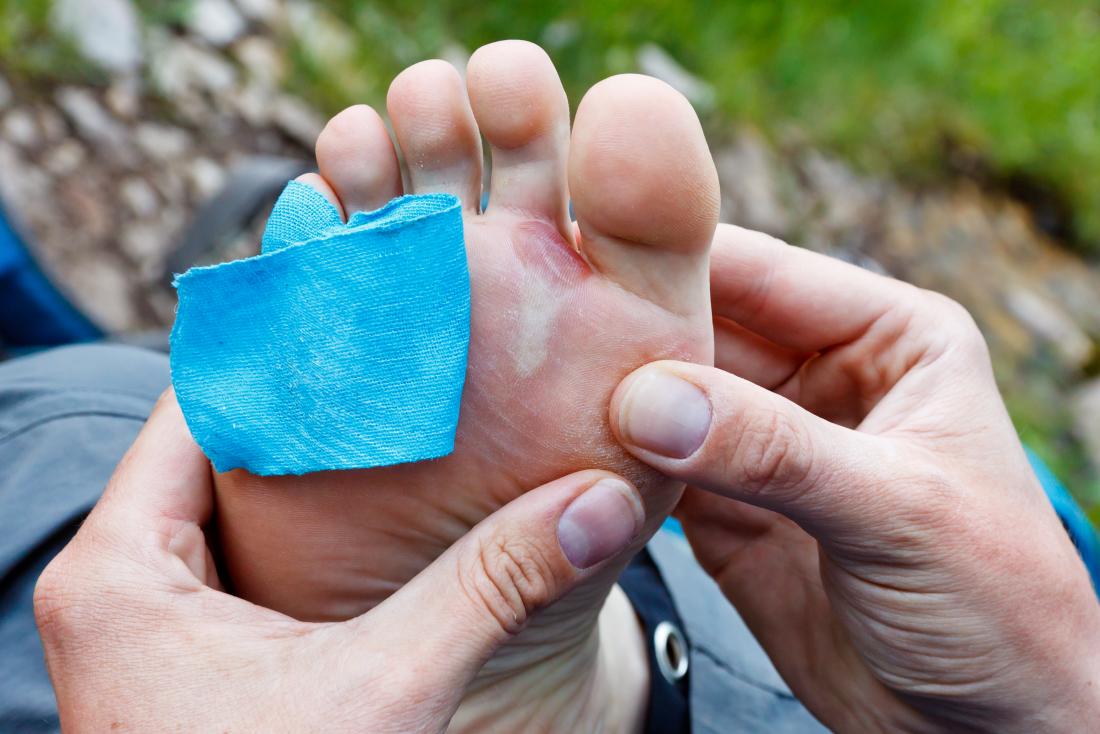
Share on Pinterest While most blood blisters do not require direct treatment, special meausres should be taken if they form on the feet or heels. wear gloves when working with tools or lifting heavy weights.People should take the following steps to reduce the risk of developing a blood blister: Preventing blood blisters involves people taking good care of their health and body and using appropriate protection in situations that require it. It is possible for nearly anyone to get a blood blister. Some causes of blood blisters in the mouth include: If someone has a blood blister in their mouth, they should see a doctor.
#DO U POP BURN BLISTERS SKIN#
minor trauma from pinching the skin between two objectsīlood blisters in the mouth are often related to another condition. poorly fitting shoes that pinch the skin. a tool or other object repeatedly rubbing against the skin. Closing a drawer on a finger or lifting heavy weights for prolonged periods can cause blood blisters. Chemical burns - can arise from skin contact with bleach, cleaning products, chemical heat packs and in some cases acid.A blood blister can form anywhere on the body where the skin is pinched but does not break open. Hot oil burns - these are common among people who use deep fryers and frying pans, usually caused by cooking oil splattering and coming into contact with skin (cooking oil can exceed 190☌). Accidents with ovens/scalding - sometimes household burns can become more severe if the burn is large in size and reaches the dermis. Severe sunburn - often happens after an extended period of sun exposure, resulting in burns of a large portion of the skin with extensive blistering. Some of the common causes of these burns include: If you experience any of the latter symptoms, it’s recommended to visit your GP/hospital for medical examination. More severe symptoms include wet-looking wounds, irregular pattern burn of the affected area, intense pain and white/deep red appearance of the skin. 
They often cause redness, pain, blistering and swelling, however, the symptoms can vary depending on the severity of this type of burn.

Second-degree burns are more serious as they don’t only affect the outer layer of the skin, but also the dermis underneath.
Friction burns - occurs from rubbing against an abrasive surface such as a carpet and can sometimes cause skin to break in more severe cases, which can increase the likelihood of infection. Electrical burns - can be caused by exposure to household current via socket openings, electrical cords & appliances (it’s recommended to see a doctor for these accidents to assess whether any internal damage has been done). Sunburn - typically caused by excessive exposure to UV rays from sun or sunlamps in tanning beds. Scalds (a type of thermal burn) - most common in young children and usually caused by hot liquid or steam. Thermal burns - usually occurs from touching hot objects such as a stove or hair straightener. Some of the common causes of superficial burns include: Typically these burns don’t break the skin but may cause redness, pain and sometimes swelling in the affected area. These burns are a common household injury and usually affect only the top layer of the skin and don’t penetrate to other tissues.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
